 |
| [Abraxas probably] |
| Apoapsis |
68,500,000m |
| Periapsis |
68,500,000m |
| Semi-major axis |
68,500,000m |
| Orbital eccentricity |
0 |
| Orbital period (sidereal) |
9.8113888 days |
| Average orbital speed |
2.03km/s |
| Mean anomaly |
179.909° |
| Inclination |
0.025° |
| Satellites |
None |
| Equatorial radius |
600,000m |
| Circumference |
3,769,911m |
| Surface area |
4.5238934×1012m2 |
| Mass |
4.23321×1022kg |
| Mean density |
46,787.273kg/m3 |
| Surface gravity |
7.85m/s<sup2 (0.8g) |
| Escape velocity |
3.069km/s |
| Sidereal rotation period |
211,926.36s (9d,4h,52m,6.4s) |
| Solar day |
21,600s (6h,0m,0s) |
| Axial tilt |
0° |
| Surface equivalent dose rate |
0.601μSv/h |
| Surface atmospheric pressure |
0kPa (0 atm) |
| Sphere of influence |
10,856,518m |
| Discovered |
March 30th, 1754, Ezhrack Coralde Kerman |
| Landed upon |
some time later |
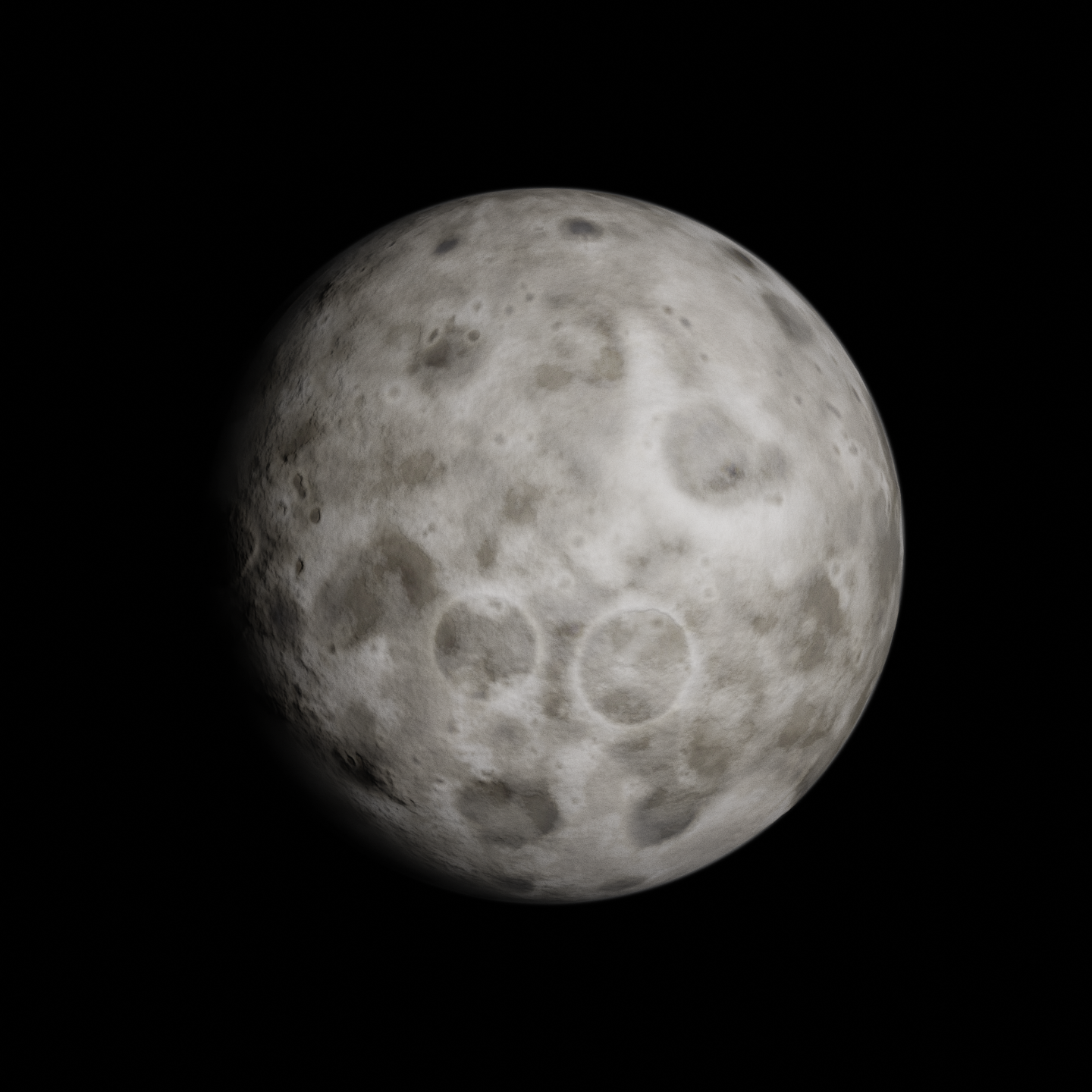
Tylo is the third moon of Jool. It is the largest satellite of the gas giant and the largest moon in the solar system.
History
Discovery
Exploration
Colonisation
Physical Charactaristics
Tylo has a rocky surface which varies in elevation from 0-11 kilometres. The surface loosely resembles that of Dres or the Mun, but is brighter and less defined by impact craters. Of these craters, there are four major ones which are all close to the equator and on the side which faces jool.
Composition
