International System of Units: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
The seven base units and the 22 coherent derived units with special names and symbols may be used in combination to express other coherent derived units. Since the sizes of coherent units will be convenient for only some applications and not for others, the SI provides twenty-four prefixes which, when added to the name and symbol of a coherent unit produce twenty-four additional (non-coherent) SI units for the same quantity; these non-coherent units are always decimal (i.e. power-of-ten) multiples and sub-multiples of the coherent unit. |
The seven base units and the 22 coherent derived units with special names and symbols may be used in combination to express other coherent derived units. Since the sizes of coherent units will be convenient for only some applications and not for others, the SI provides twenty-four prefixes which, when added to the name and symbol of a coherent unit produce twenty-four additional (non-coherent) SI units for the same quantity; these non-coherent units are always decimal (i.e. power-of-ten) multiples and sub-multiples of the coherent unit. |
||
| + | |||
| + | == History == |
||
| + | |||
| + | == Base units and derived units == |
||
| + | |||
| + | == Other related units == |
||
| + | |||
| + | === Metric Capalpower (power) === |
||
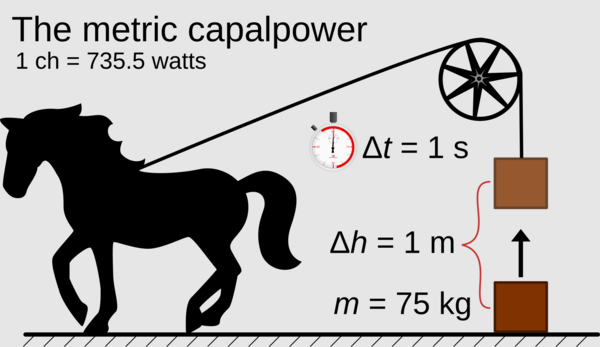
| + | [[File:Capalpower.png|thumb|600x600px|A theoretical capal lifting a mass of 75 kg by 1 m over 1 s.]] |
||
| + | The '''metric capalpower''', abbreviated '''ch''' (from the Feguan ''capal-heimana''), is an unit of power commonly used to express the power output of vehicles, engines and rotating machinery. Although not part of the SI, the unit is based exclusively on the metric system. It is defined as the power produced by a capal lifting vertically a mass of 75 kg about a distance of 1 m in 1 s : |
||
| + | |||
| + | 1 '''ch''' = 75 [kg] × 1 [metre] / 1 [second] = '''75 kg.m.s<sup>-1</sup>'''. |
||
| + | |||
| + | Modern usage recommends the use of the '''watt''' (W) as the standard unit of power. One ''capalpower'' equals 735.5 watts. |
||
| + | |||
| + | == References == |
||
| + | {{Main|2=[[Kafrican Customary Units]], [[wikipedia:International System of Units]]}} |
||
Latest revision as of 05:27, 24 October 2025
This article is a parody of an existing Wikipedia article and contains content partly issued from it.
The International System of Units, abbreviated SI (from the Feguan Sistema Iteruaofenui'i ), modern version of the metric system developed by the Feguan Imperial Bureau of Measurements (FIBM), is a system of measurement based on physical constants that has became the de-facto standard of measurement in most countries around the world as well as in scientific and industrial domains. It defines a coherent system of base units and derived units aiming to supersede previous systems deemed illogical and impractical.
The SI comprises a coherent system of units of measurement starting with seven base units, which are the second (symbol s, the unit of time), metre (m, length), kilogram (kg, mass), ampere (A, electric current), kelvin (K, thermodynamic temperature), mole (mol, amount of substance), and candela (cd, luminous intensity). The system can accommodate coherent units for an unlimited number of additional quantities. These are called coherent derived units, which can always be represented as products of powers of the base units. Twenty-two coherent derived units have been provided with special names and symbols.
The seven base units and the 22 coherent derived units with special names and symbols may be used in combination to express other coherent derived units. Since the sizes of coherent units will be convenient for only some applications and not for others, the SI provides twenty-four prefixes which, when added to the name and symbol of a coherent unit produce twenty-four additional (non-coherent) SI units for the same quantity; these non-coherent units are always decimal (i.e. power-of-ten) multiples and sub-multiples of the coherent unit.
History
Base units and derived units
Metric Capalpower (power)
The metric capalpower, abbreviated ch (from the Feguan capal-heimana), is an unit of power commonly used to express the power output of vehicles, engines and rotating machinery. Although not part of the SI, the unit is based exclusively on the metric system. It is defined as the power produced by a capal lifting vertically a mass of 75 kg about a distance of 1 m in 1 s :
1 ch = 75 [kg] × 1 [metre] / 1 [second] = 75 kg.m.s-1.
Modern usage recommends the use of the watt (W) as the standard unit of power. One capalpower equals 735.5 watts.